 Nous contacter
Nous contacter
Advice
CERTIFICATION OF FRUIT PLANTS
| Download the advice sheet | |
| « CERTIFICATION OF FRUIT PLANTS » | |
 |
The marketing of fruit plants within the European Union is subject to several regulations:
➢ the Plant Health Regulation,
➢ the Plant Marketing Directive.
The plant passport
A fruit plant can only leave the nursery to be delivered to custom-ers in the European Union if it is accompanied by a Plant Passport (PP) which must accompany the plants. In practice, in the case of grafted fruit plants, this PP will be found on the label of the bundle or of the individual plant.

The elements of the plant passport:
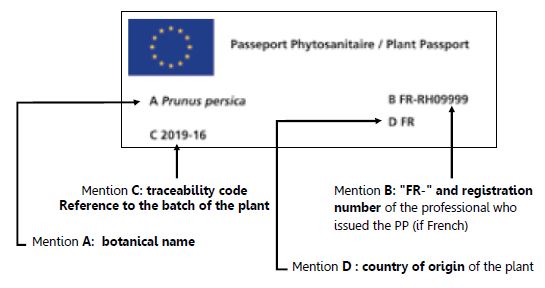
The PP is governed by the Plant Health Regulation since 2019 throughout the EU. This regulation classifies diseases and pests into different categories, including quarantine pests (QP) and regulated non-quarantine pests (RNQP).
For example, Plum pox is classified as a RNQP and Xylella as a QP. The Plant Health Regulations govern the observation and analysis of diseases, which may be visual or carried out in laboratories ap-proved for the various diseases.
Checks are made throughout the production cycle of the plant.
Since 2021, the CTIFL is the competent authority for all French nurseries involved in the certification of fruit plants, for both certi-fied and CAC material.
Certification of plant material
The phytosanitary regulation is accompanied by a regulation on the marketing of plant material which requires seedlings to be CAC or certified in order to be able to circulate in the EU.
COMMUNITY AGRICULTURAL CONFORMITY
Community Agricultural Conformity (CAC) is the minimum stand-ard. CAC trees come from an establishment recognised for its pro-fessionalism and using good sanitary practices, traceability, multi-plication and varietal authenticity. These CAC plants are now con-trolled by the CTIFL, but as part of a 2nd level control.
Example of a CAC plant label:

EUROPEAN CERTIFICATION
Certification was a national system until European certification came into force in 2017. The 2 pillars of the European certification are:
• The absence of all diseases and viruses listed in the certification specifications.
• Controlled varietal authenticity.
THE INFEL® CERTIFICATION
However, French nurserymen have worked with the CTIFL to set up an even higher level of certification: INFEL® certification.
The INFEL® certification differs from European certification in that:
• a greater number of pathogens are controlled and controls are stricter,
• a limitation of the lifespan of the graftwood orchards,
• individual labelling of the plants checked in the nursery before being lifted,
• minimum plant size requirements.
Example of an INFEL® certified plant label:

In France, certified and INFEL® certified plants are inspected by the CTIFL, as part of a first level control plan.
Our advice : as the labels of certified plants are printed by the CTIFL, we do not have a copy and cannot provide a duplicate. When planting, keep a few labels of each batch, with the delivery note, in your files.


Archive of Pommoscopes
Request Quotation - CERTIFICATION OF FRUIT PLANTS
 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Italiano
Italiano Русский
Русский Polski
Polski





